3D manufacturing
Nano to Micro/Macro (3D shaping)
@
provided by:
Instruments datasheets
EURONANOLAB
France
3D MF at EURONANOLAB - LAAS
EURONANOLAB
France
3D MF at EURONANOLAB - FEMTO-ST
@
provided by:
Also consider
Structural & Morphology Characterization
SEM Scanning Electron Microscopy
In SEM a beam is scanned over a sample surface while a signal from secondary or back-scattered electrons is recorded. SEM is used to image an area of the sample with nanometric resolution, and also to measure its composition, crystallographic phase distribution and local texture.
Nano to Micro/Macro
LSIVP Laser surface and in-volume Patterning
Laser patterning is a technique for the controlled patterning of materials at micro- and nano-scales. It offers the ability to directly write patterns on the surface and complex 3D channels into the bulk of solid materials, also biomaterials. Applications can range from microfluidic systems and sensors to tissue engineering scaffolds.
Nano to Micro/Macro
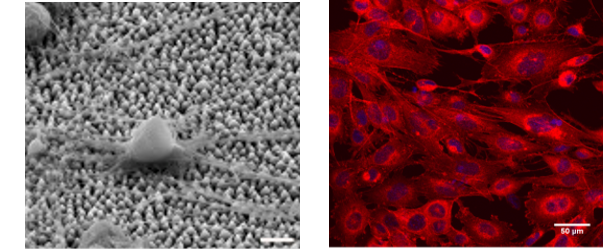
CCF Cell culture facilities
The Cell Culture Facility provides the necessary equipment (basic cell culture, sample preparation, functional assays and imaging equipment) for the study of the effect of biomaterials on specific cell behavior and function and cellular responses, such as cell survival, adhesion, morphology, proliferation, growth, migration and differentiation.
Nano to Micro/Macro
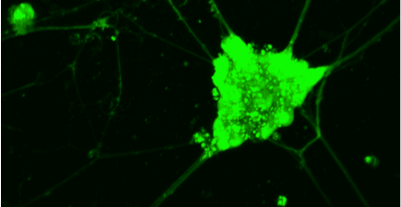
LCI Live cell imaging
The “Live Cell Imaging” facility is equipped with advanced imaging microscopy techniques (based on two- or multi- photon excitation), which are appropriate for the all-optical minimally invasive, high-resolution (<500nm), deep (>500μm) monitoring of living cells and tissues for long periods of time.
Structural & Morphology Characterization
CM Confocal microscopy
Confocal microscopy (CM) is an optical imaging technique that creates a virtual plane or slice, many micrometers deep within the analyzed sample. Compared to conventional microscopy, it provides fine detailed images of higher quality and with more contrast. In addition, virtual 3-D images of the analyzed microstructure can be obtained.