A set of techniques and extensive know-how are offered to disperse nanoparticles as oxides, metals, carbon nanostructures, paraffins in fluids as water, glycol, oils, by combining expertise in selecting proper surfactants with various dispersion processes:
- Tip sonication with various tips and flow cell to sonicate from few ml to liters
- high pressure homogenization
- planetary ball milling.
i
@
provided at NFFA-Europe laboratories by:
i
@
provided at NFFA-Europe laboratories by:
Also consider
Structural & Morphology Characterization
SEM Scanning Electron Microscopy
In SEM a beam is scanned over a sample surface while a signal from secondary or back-scattered electrons is recorded. SEM is used to image an area of the sample with nanometric resolution, and also to measure its composition, crystallographic phase distribution and local texture.
Theory & Simulation
SGSEP Structural and ground-state electronic properties
This technique offers the possibility of simulating structural and electronic properties based on the electronic ground state, including electronic charge analysis, energetics of formation, structural and vibrational properties; IR, Raman, EPR, NMR, core-level XAS & XPS, STM & AFM.
Electronic & Chemical & Magnetic Characterization
OS Optical spectroscopy
VUV/UV/Vis/NIR spectroscopy is the measurement of the attenuation of a beam of light after it passes through a sample or after reflection from a sample surface. It is useful to characterize absorption, transmission, and reflectivity of a variety of technologically important materials, such as gases, film, pigments, coatings, windows, and filters.
Electronic & Chemical & Magnetic Characterization
PL PhotoLuminescence
PL is a non-contact, non-destructive method of probing the electronic structure of materials, often used in the context of semiconductor devices to determine the bandgap energy, the composition of heterostructures, the impurity levels, the crystal quality, and to investigate recombination mechanisms.
Growth & Synthesis
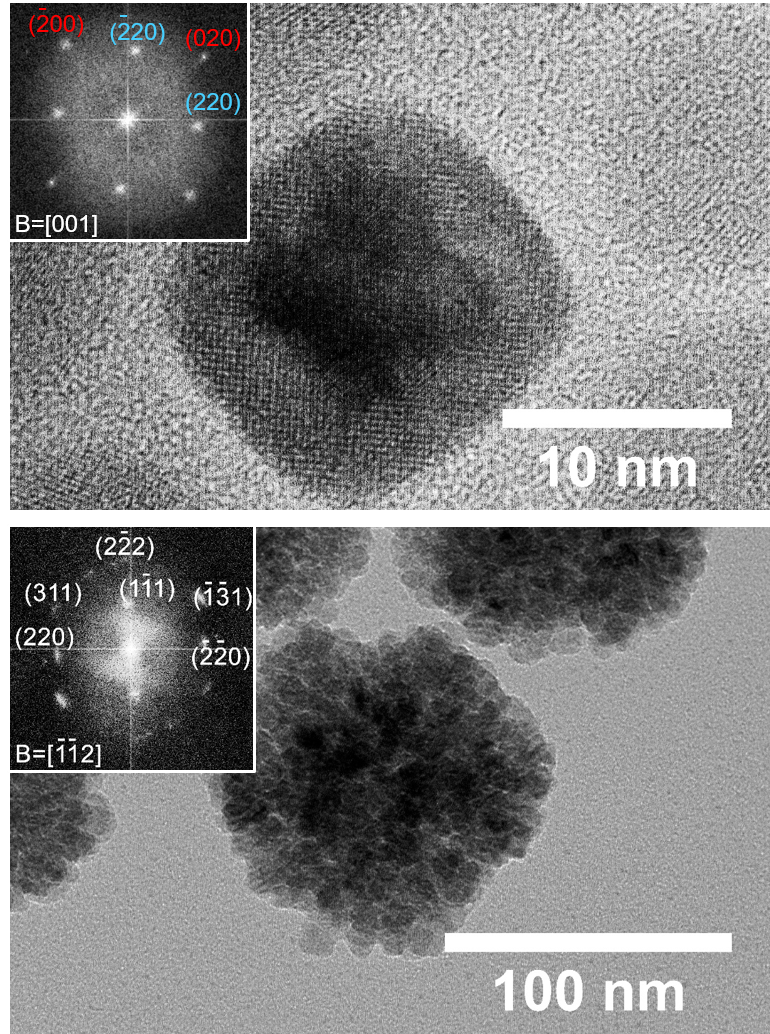
GIN Growth of inorganic nanocrystals
The nanochemistry facility exploits elaborate bottom-up colloidal chemistry approaches that harness nanoscale size and shape-guiding mechanisms to afford various kinds of inorganic nanocrystals with tunable response (cf. semiconducting, plasmonic, magnetic).