Chemical analysis
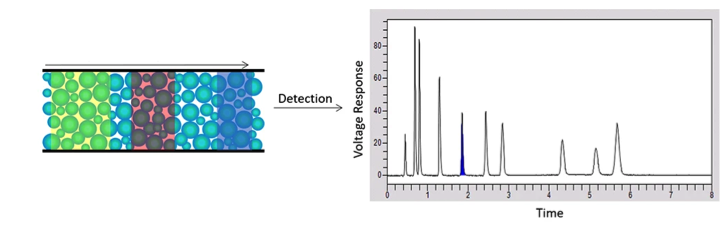
HPLC HPLC with CAD, UV and Fluorescence detectors(Chemical composition analysis)
HPLC is analytical technique to separate, identify, and quantify molecules in a mixture. Dissolved components are pumped into a packed column where they are separated from each other due to their different degrees of interaction with the packing material. HPLC-UV/MS can be used for the detection and quantification of organic contaminants in water.
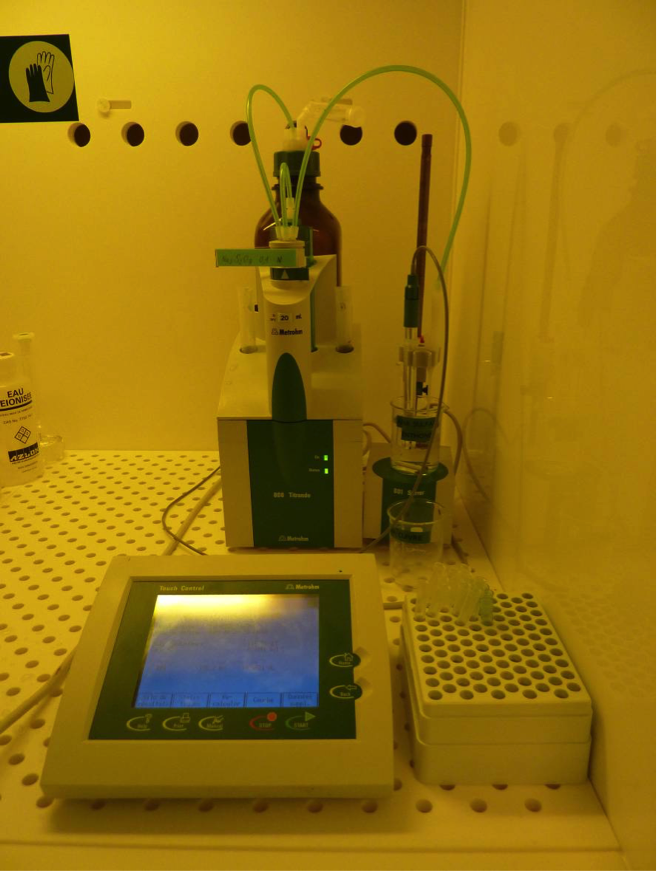
AT Automated Titration
Titration is an analytical technique that allows the quantitative determination of a specific substance (analyte) dissolved in a sample. This technique is based on a complete chemical reaction between the analyte and a reagent (titrant) of known concentration, added to the sample.
ICP-MS ICP Mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS) (single particle analysis, trace element analysis)
ICP-MS allows measuring elements at trace levels. Dissolved sample is introduced into an argon plasma where the molecules are dissociates and further ionized. Singly-charged ions thus formed are directed into the mass spectrometer. A special application of ICP-MS (spICP-MS) allows measuring size and number concentration of a particle suspension.
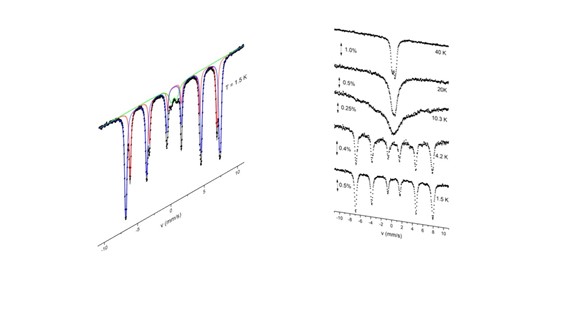
MOS Mossbauer spectroscopy
Mössbauer spectroscopy is used for the characterization of electronic and magnetic properties of materials containing specific isotopes such as 57Fe, including alloys and oxides, magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic storage and biomedical applications, synthetic and natural minerals and ores, and iron-containing biological systems and thin films.