Engineering of colloids
Nano to Micro/Macro (Synthesis of dispersed-phases)
The engineering of colloids allows to obtain colloids, nanofluids, emulsions, gels which have various applications ranging from microfluidics, to life sciences, energy, environmental technology etc. It represents the first step required to produce inks, pastes and/or suspensions for the subsequent application, either in form of coating or 3D structures. The control of colloidal stability and surface charge interactions among the involved phases enable to optimize the design strategy and the final functional performance.
Available techniques:
- dispersion of nanoparticles in water, glycols, oils by the proper selection of surfactants and by various dispersion processes (sonication, high pressure homogenization, ball milling)
- heterocoagulation: inorganic nanoparticles with opposite surface charge can be closely coupled promoting the formation of composite or hybrid materials enabling new syngergistic effects
@
provided at NFFA-Europe laboratories by:
Instruments datasheets
CNR-DSCTM
Italy
Engineering of colloids at ISSMC
@
provided at NFFA-Europe laboratories by:
Also consider
Structural & Morphology Characterization
NLM Nonlinear microscopy
NLM takes advantage of tightly focused ultra-short laser pulses (fs) to excite non-linear optical phenomena like Second Harmonic Generation, Third Harmonic Generation, Two-Photon and Three-photon excited Fluorescence. Along with laser raster-scanning of the sample, non-linear imaging microscopy of large areas is accomplished within seconds.
Structural & Morphology Characterization
CM Confocal microscopy
Confocal microscopy (CM) is an optical imaging technique that creates a virtual plane or slice, many micrometers deep within the analyzed sample. Compared to conventional microscopy, it provides fine detailed images of higher quality and with more contrast. In addition, virtual 3-D images of the analyzed microstructure can be obtained.
Growth & Synthesis
GIN Growth of inorganic nanocrystals
The nanochemistry facility exploits elaborate bottom-up colloidal chemistry approaches that harness nanoscale size and shape-guiding mechanisms to afford various kinds of inorganic nanocrystals with tunable response (cf. semiconducting, plasmonic, magnetic).
Structural & Morphology Characterization
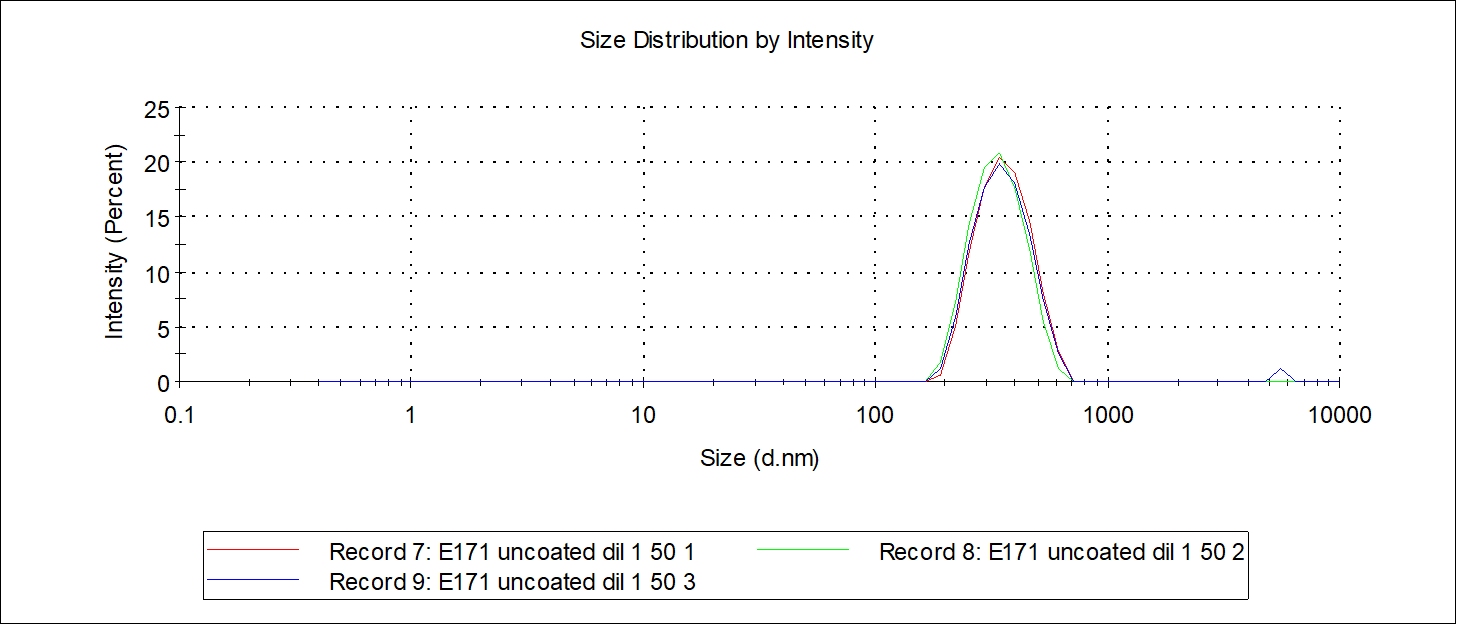
DLS Dynamic Light Scattering
DLS is a powerful tool for investigating the diffusion behaviour of macromolecules or particles in suspension polar or non-polar liquid media. It gives an estimate of the size of the particles by means of mathematical relations between light scattering and diffusion behaviour of particles.