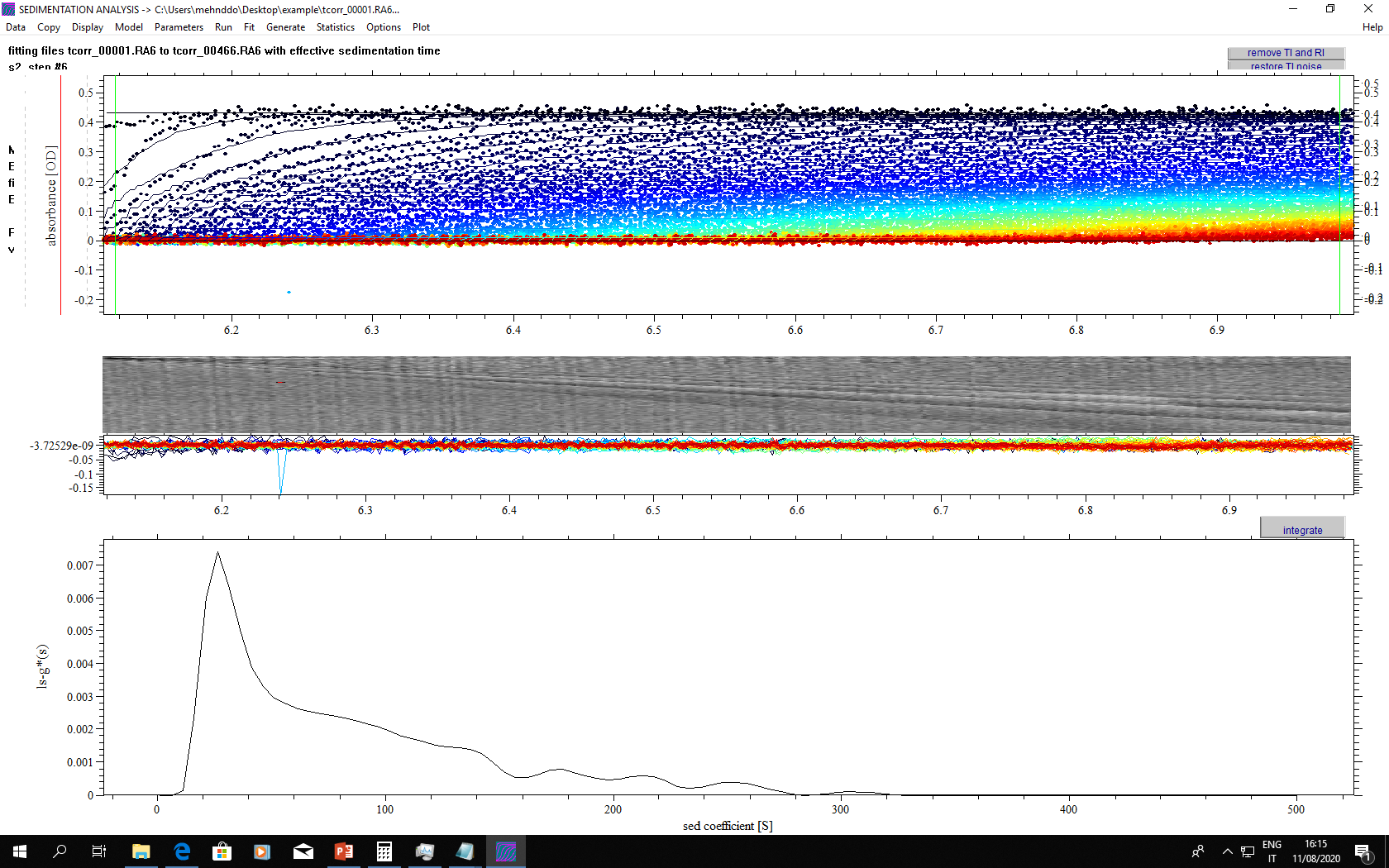
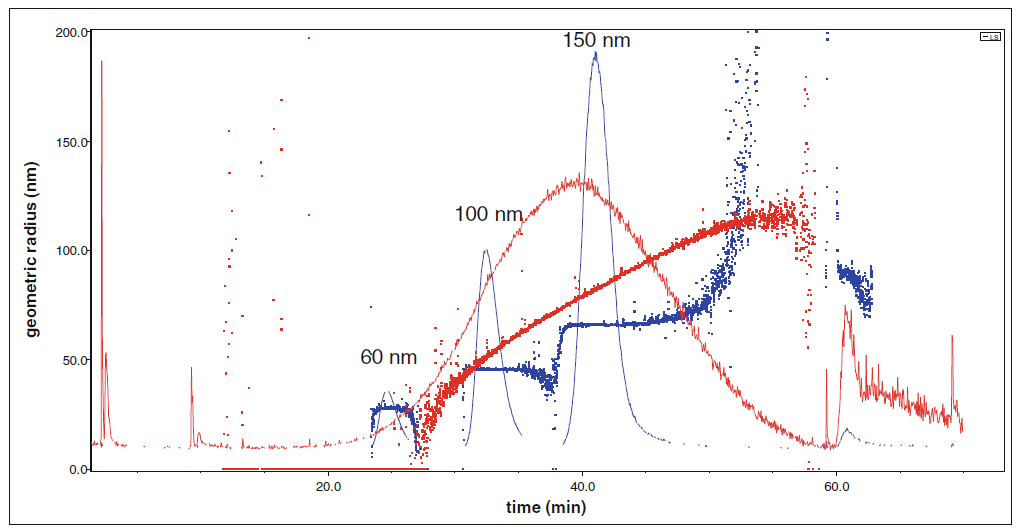
The technique measures sedimentation speed of particles in a liquid under the gravitational force generated in an ultracentrifuge. AUC detects light extinction and/or refractive index change and calculates equivalent sphere diameters applying the Stokes equation. As the calculation is based on first principles, no size calibration is needed. Sedimentation coefficient distributions calculated from interference measurements can be transformed to mass based distributions needing only density as input parameter. The particle suspension is loaded in a sample holder with transparent optical windows. Reference liquid (solvent) is loaded in the adjacent cell of the sample holder. Sample holders are placed in a rotor and sedimentation of the particles in the applied gravitational field (at a rotation speed in the range of 1100-50000 rpm) is monitored by interference and/or absorbance optics. The size distribution of floating particles, like lipid nanocarriers or liquid droplets in emulsion can be calculated from their floatation speed. Density of particles can be determined by a series of measurements in various density liquids (sucrose solution, D2O/H2O mixture).
i
@
provided at NFFA-Europe laboratories by:
i
@
provided at NFFA-Europe laboratories by:
Also consider
Electronic & Chemical & Magnetic Characterization
XPS X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
XPS is a surface spectroscopic technique for quantitative measurements of the elemental composition or stoichiometry and the chemical state of the present elements, like their oxidation state and chemical bonds. XPS is highly surface sensitive, giving chemical and binding energy information from the a narrow region close to the surface.
Structural & Morphology Characterization
SAXS Small Angle X-ray Scattering
SAXS is a non-destructive and versatile method to study the nanoscale structure of any type of material (solid, liquid, aerosols) ranging from new nanocomposites to biological macromolecules. Averaged particle sizes, shapes and distributions, porosity, degree of crystallinity and electron density maps with nanometer precision can be obtained.
Structural & Morphology Characterization
SIMS Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry
By SIMS, samples are bombarded; sputtered and ionized atoms accelerate towards a mass spectrometer, providing surface mass spectra, images with lateral resolution in the 0.1 to 10 µm range and depth profiles with depth resolution in the 1 to 10 nm range. SIMS can be quantitative up to ppb sensitivity when reference samples are used.
Electronic & Chemical & Magnetic Characterization
Ellipsometry Ellipsometry
Ellipsometry is a contact-free, nondestructive method for characterization of the dielectric and optical properties (refractive index, absorption and thickness) of layered nanostructures in the size range of < 1 nm to several μm.
Structural & Morphology Characterization
MALS Multi Angle Light Scattering (MALS) (nanoparticle sizing)
MALS is a technique for measuring light scattered by a sample into a plurality of angles. It is used to determine both the absolute molar mass and the average size of molecules in solution. MALS is typically used as a flow-mode detector coupled to Asymmetric Flow Field Flow fractionation (AF4) or Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC).