Small Angle Neutron Scattering (temporarily unavailable)
Structural & Morphology Characterization (Neutron characterisation)
Due to a damage at the tube of the central channel, the MLZ will have neutrons again not before August 2022. For this reason, the instruments at the MLZ will not be available in the next NFFA-Europe Pilot call for proposals. We will keep you updated.

@
provided at Large Scale Facilities by:

@
provided at Large Scale Facilities by:
Also consider
Electronic & Chemical & Magnetic Characterization
XPS X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
XPS is a surface spectroscopic technique for quantitative measurements of the elemental composition or stoichiometry and the chemical state of the present elements, like their oxidation state and chemical bonds. XPS is highly surface sensitive, giving chemical and binding energy information from the a narrow region close to the surface.
Structural & Morphology Characterization
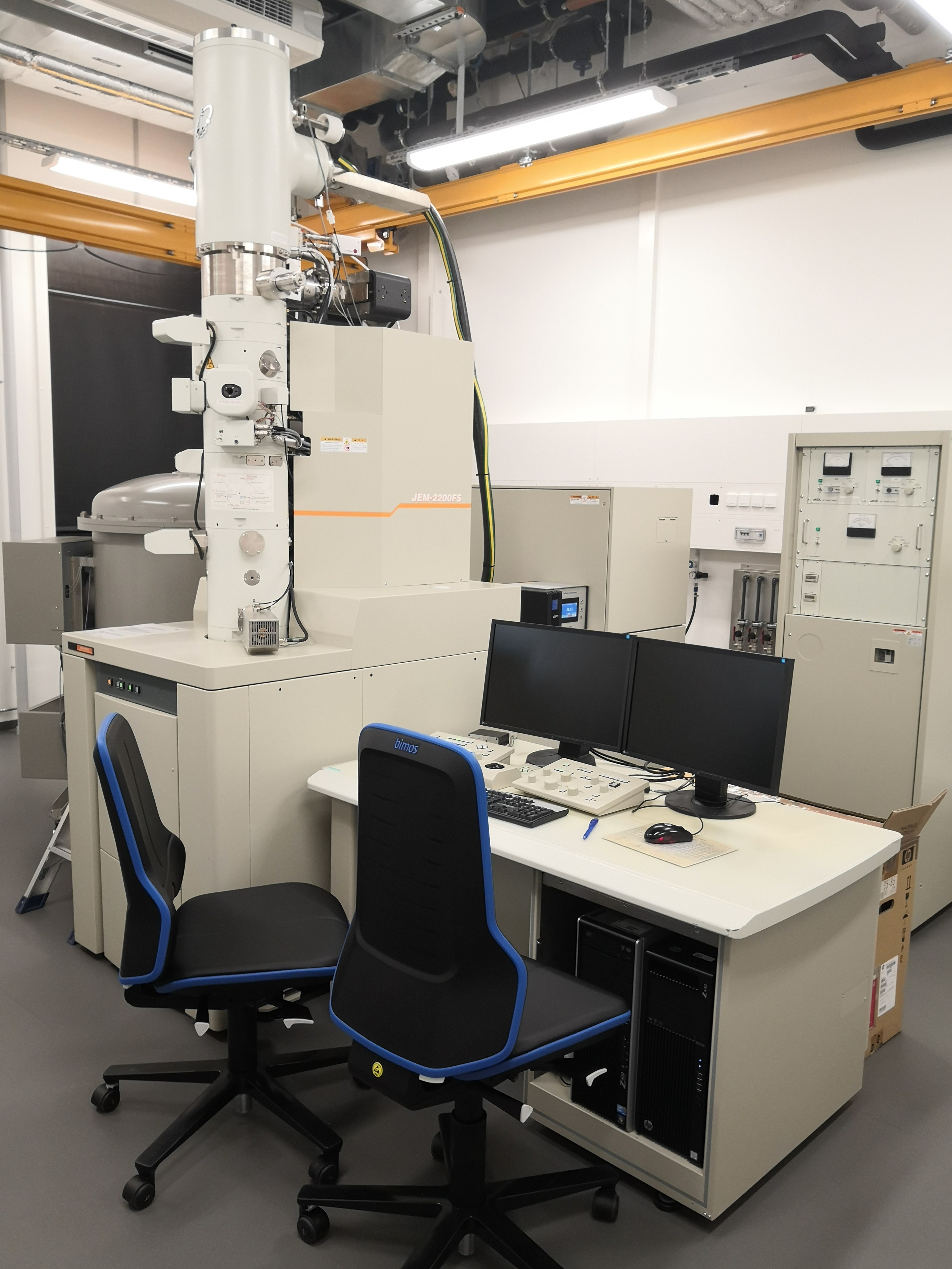
Cryo-TEM Cryo-Transmission Electron Microscopy
Cryo-Transmission electron microscopy is a technique for soft matter studies allowing real space investigations about shape and size distribution of particles, self-assembly and aggregation. Liquid sample can be directly observed on grid after blotting. An automatic plunge freezer is used to make cryo-specimen for direct imaging (Cryo-DI).
Structural & Morphology Characterization
SAXS Small Angle X-ray Scattering
SAXS is a non-destructive and versatile method to study the nanoscale structure of any type of material (solid, liquid, aerosols) ranging from new nanocomposites to biological macromolecules. Averaged particle sizes, shapes and distributions, porosity, degree of crystallinity and electron density maps with nanometer precision can be obtained.
Electronic & Chemical & Magnetic Characterization
PL PhotoLuminescence
PL is a non-contact, non-destructive method of probing the electronic structure of materials, often used in the context of semiconductor devices to determine the bandgap energy, the composition of heterostructures, the impurity levels, the crystal quality, and to investigate recombination mechanisms.
Electronic & Chemical & Magnetic Characterization
FS Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Fluorescence is a type of luminescence caused by photons exciting a molecule, raising it to an electronic excited state. Fluorescence spectroscopy analyzes fluorescence from a molecule based on its fluorescent properties.