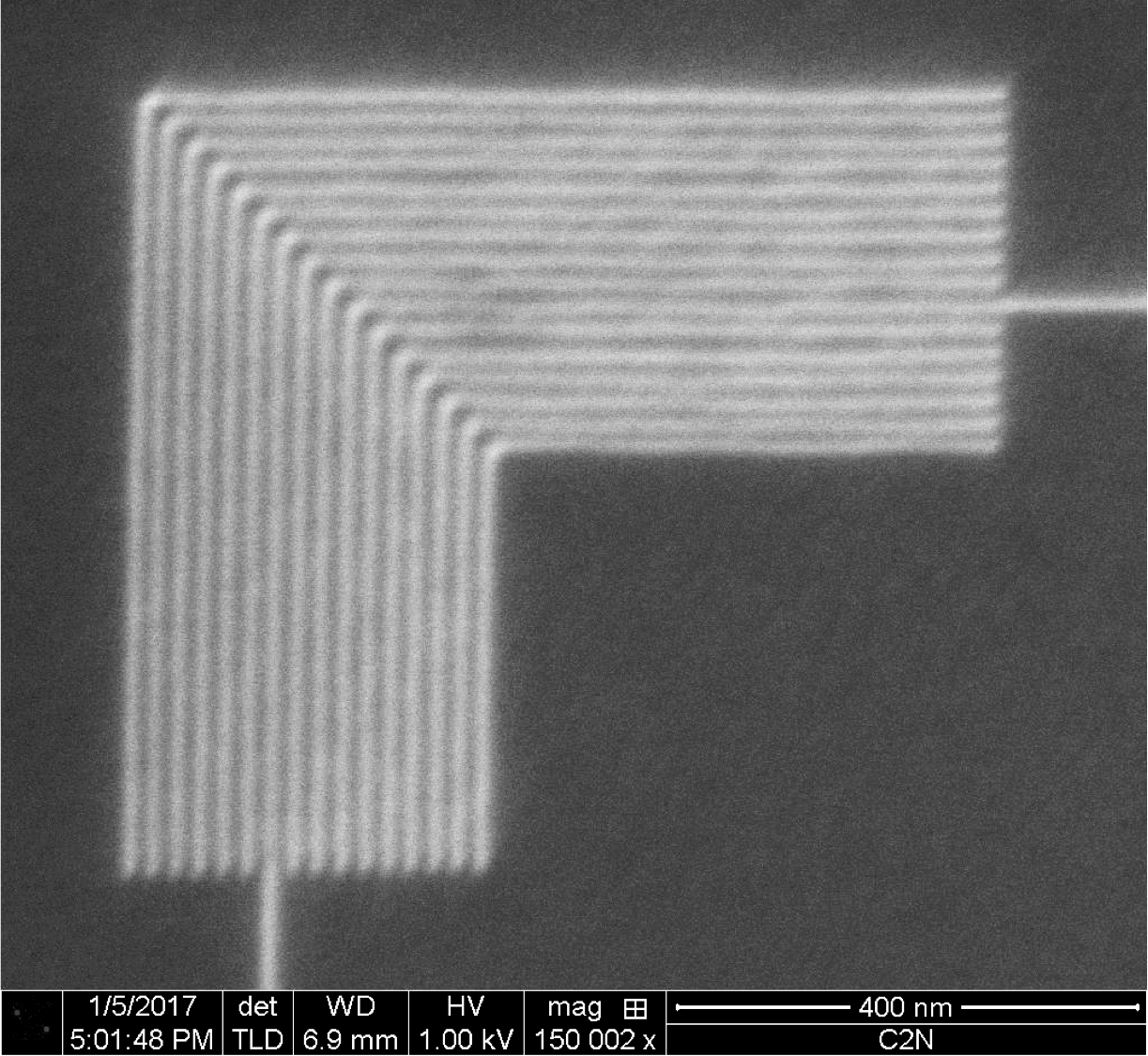
Individual atoms are stripped away from a finely sharpened needle until an atomic pyramid is created with just three atoms at the very end of the source tip – a configuration called the trimer. Once the trimer is formed, the tip is maintained under high vacuum and cryogenic temperatures with helium or neon gas flowing over it. By applying a high voltage to the needle, the He or Ne atoms are ionized in the vicinity of a single atom. This produces an extremely bright beam that can be focused with an advanced electrostatic column to an extraordinarily small probe size. He and Ne atoms have a smaller De Broglie wavelength and a smaller area of surface interaction than electrons and can, therefore, achieve higher resolution. With the use of an electron flood gun charge compensation can be achieved for use with insulating materials. Patterning can be performed by direct milling (material removal) with the He or Ne atoms or by exposing a resist without any proximity effects as is usually the case with electron beam lithography. The technique can also be used for additive nanopatterning, where high-quality conductive and insulating materials can be deposited with ion-beam induced deposition. Since He or Ne is used, undesirable Ga-implantation does not occur leading to high material purity and minimized changes to the properties of the materials. In addition, the tool can be used for high-resolution imaging (0.5 nm) with very large depth of focus.
i
@
provided at NFFA-Europe laboratories by:
i
@
provided at NFFA-Europe laboratories by:
Also consider
Structural & Morphology Characterization
SEM Scanning Electron Microscopy
In SEM a beam is scanned over a sample surface while a signal from secondary or back-scattered electrons is recorded. SEM is used to image an area of the sample with nanometric resolution, and also to measure its composition, crystallographic phase distribution and local texture.
Electronic & Chemical & Magnetic Characterization
XPS X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
XPS is a surface spectroscopic technique for quantitative measurements of the elemental composition or stoichiometry and the chemical state of the present elements, like their oxidation state and chemical bonds. XPS is highly surface sensitive, giving chemical and binding energy information from the a narrow region close to the surface.
Structural & Morphology Characterization
AFM Atomic Force Microscopy
AFM is a surface sensitive technique permitting to obtain a microscopic image of the topography of a material surface and certain properties (like friction force, magnetization properties…). Typical lateral image sizes are within a range of only a few Nanometers to several Micrometers, and height changes of less than a Nanometer.
Lithography & Patterning
EBL Electron Beam Lithography
Electron-beam lithography is a direct write nanopatterning technique utilizing a finely focused electron beam in order to write nanoscale patterns on special e-beam resists in two and three dimensions. Compared to other nanostructuring methods, it stands out for its high level of flexibility and resolution and reasonable patterning speed.